Ministry of Higher Education
صندوق مشروع تطوير التعليم العالى
Enhancement of Teaching Anatomy by Plastination
Technology of Plastination
A New Method of Teaching Anatomy
By
Aly Eldeen Abd Elbasset Aly

ETAP
B-053-TO
WORKSHOP ON PLASTINATION
(
Faculty of Veterinary Medicine
Zagazig Plastination
Laboratory
Introduction
The biological materials
after death decomposes by autolysis and putrefaction. Since the
beginning of our life , trials have been
mad to keep the body in normal shape ,to keep the mortal frame for coming back
to life later e.g. Egyptian mummification 6000 B.C. and cryo-preservation in
modern life. Fixation by formalin was discovered by Blum 1896 ,which protect
the cadavers against deterioration. Disadvantage of formalin include smell ,
shrinkage and discoloration of the tissue .Formalin ,however, is still mainly
used for preservation in Anatomy
Department because of its price and
preservation properties.
In 1978
Gunther von Hagens invented Plastination in Heidelberg University , Germany.
What is Plastination? - A method of preserving perishable
biological specimens by replacing the tissue water and lipid with a curable
plastic polymer. The specimens preserved in this manner are permanent, clean,
non-toxic and dry.
Why is it useful in Anatomy?
- Plastinated specimens retain textures and structures of tissue and are
therefore an invaluable teaching resource in anatomy. Plastinated specimens
have none of the usual hazards and restrictions associated with the study of
anatomical specimens eg. use of gloves, toxic fumes, contagions etc, and are
more robust than the original specimen.
Theory and Procedures(Von Hagens G. 1985)
In Plastination process, water and lipids in biological tissues are
replaced by curable polymers (silicone, epoxy, polyester) which are
subsequently hardened, resulting in dry, odorless and durable specimens. The
class of polymer used determines the optical (transparent or opaque) and
mechanical (flexible or firm) properties of the impregnated specimen.
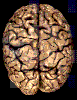
Silicone is used for whole specimens and
thick body and organ slices to obtain a natural look. (Plate I,II,III,IV,V)

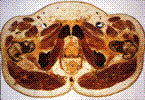
Epoxy resins are used for thin,
transparent body and organ slices. (Plate VI,VII)

Polyester-copolymer is exclusively used for brain
slices to gain an excellent distinction of gray and white matter.
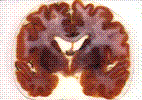
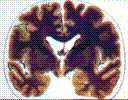
The
technique consists of four main steps:
Fixation can be done by almost all
conventional fixatives.
Dehydration is achieved mainly by acetone because
acetone also serves as the intermediary solvent during impregnation.
Forced impregnation is the central step in
plastination: vacuum forces the acetone out of and the polymer into the
specimen.
Hardening (Curing): Finally the impregnated specimen is
hardened by exposing it to a gaseous hardener (silicone), or by UVA-light and
heat (polyester, epoxy). Plastinated specimens are perfect for teaching,
particularly for neuroanatomy. Silicone plastinated brains are useful
because they can be grasped literally and they are almost everlasting.
Polyester plastination of brain slices provides an excellent distinction of
gray and white matter and thus a better orientation.
Plastination is carried out in many
institutions worldwide and has obtained great acceptance particularly because
of the durability, the possibility for direct comparison to CT- and MR-images, and
the high teaching value plastinated specimens have.
If a university takes the decision
and commitment to help this project the results will be excellent and useful
for new students who will shape the future in research,clinical knowledge and
teaching.
References:
Aly Eldeen Abd Elbasset
Aly,Alexander Probst, Mircea-Constantin Sora und
Horst Erich König
( Oktober ,2005 )
Plastination-reale Abbilder Lebender Structuren.
Zeitschrift
der Veterinärmedizinischen Univ. Wien,Heft 03/05
Blum 1896:Cited by
Weiglein,AH.2001:Preservation of Biological Tissue:Yeterday-
Today-Tomorrow.J.Int.Soc.Plastination16:31-41,2001.
F.Elnady and A.E.Basset Aly
(2003)
Plastination in Teaching Veterinary Anatomy
Abstract book of the Twenty-seventh
Scientific Conference
of The
Egyptian Anatomical Society (December 2003).
Von Hagens G. 1985:
Leaflets for
Plastination.Heidelberg,Germany:Anatomische
Institut
. 1,Universitat Heidelberg.
تكنولوجيا
البلستكه
طريقه
حديثه لتدريس ماده التشريح
أ.د.على
الدين عبد الباسط على
معمل
البلستكه بالزقازيق
كليه
الطب البيطرى جامعه الزقازيق
البلستكه
هى احدى طرق حفظ العينات التشريحيه عن طريق استخراج ا لمياه والدهون من الانسجه
بواسطه االاسيتون فى درجات حراره منخفضه واحلال البلاستيك بأنواعه داخل الانسجه عن
طريق احداث ضغط سالب.
اكتشفت
هذة الطريقة عام 1980 فى جامعة هيدلبيرج- المانيا.
و
يلاحظ ان العينات سهلة فى التداول و تستخدم بصورة سهلة للتدريس فى معظم الجامعت
العالمية. و لقد اثبتت الدراسات جدوى استخدام هذة الطريقة فى تدريس العلوم
التشريحية و البيلوجية.
ولقد تم انشاء معمل للبلستكة بكلية
الطب البيطرى – جامعة الزقازيق
Zagazig Plastination Laboratory
لانتاج عينات لتدريس مادة التشريح لكليات الطب
البيطرى و الطب البشرى. و ذلك بتمويل من صندوق تطوير التعلبم العالى HEEPF مشروع كود
B-053-T0 .
يشارك فى المشروع اساتذه من جامعات الزقازيق, القاهرة ،أسيوط،
أسكندرية.كما
يشارك اساتذة من فينا وجمعيه
البلستكه الدوليه
International Society
of Plastination , ISP
و هذة العينات تصلح لتدريس مواد التشريح و الباثولوجيا و الجراحة و الطب الشرعى وفحص اللحوم و البيولجى.
